Intelligent World 2030: How Will You Experience Healthcare in the Future?
In this series of blog posts, we’ll be looking at our predictions for the “8 Outlooks” in our Intelligent World 2030. These examine how technology will shape key aspects of work and life over the next decade and what that means for you.
Read the introductory post 8 Outlooks for Intelligent World 2030 for more on what we’ll be covering.
A Shot in the Arm for Health
Over the past decade, humanity’s health as a whole has changed significantly. Life expectancy has increased, child mortality rates have dropped, and the pace of population aging is accelerating worldwide.
According to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) World Health Statistics 2021 report, global life expectancy has increased from 66.8 years in 2000 to 73.3 years in 2019, while projections indicate that 16.5% of the global population will be over 60 years old by 2030. This presents a whole new set of challenges.
New Challenges
An older population indicates an increase in demand for healthcare services. But by 2030, there will be a global predicted shortfall of 5.7 million nurses and 18 million health workers.
There is also an uneven distribution of medical resources and access to healthcare across the world.
By 2030, there will be a global predicted shortfall of 5.7 million nurses and 18 million health workers.
To help address these issues, we explore three directions when it comes to technology in healthcare in our Intelligent World 2030 report:
- using computing technologies to identify potential health problems
- precision medicine and treatment plans
- using cloud-edge-device synergies to make healthcare services location- independent.
With most people now being able to enjoy long lifespans, we need to ensure a better quality of life by improving our “healthspans”.
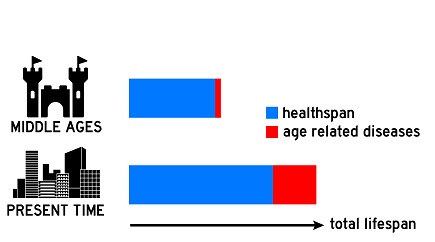
Preemptive Strike
According to the WHO, 60% of illnesses are caused by lifestyle factors and 7 out of 10 people now die from non-communicable diseases, which means that we should start shifting our focus from treatment to prevention.
Real-time health monitoring and health data modeling can help us cultivate healthier lifestyles and consciously weave disease prevention into the fabric of our daily lives.
- By 2030, it is expected we will be able to track our body’s physical indicators in real time with sensitive biosensor technologies and intelligent devices.
- Technologies such as Big Data and IoT will enable doctors to build knowledge graphs based on users’ data, including health indicators, medical diagnoses, and treatment results.
- Health knowledge graphs will simultaneously allow us to manage our health independently, reducing a reliance on doctors. Paired with IoT and AI, personal health data modeling is now realistic prospect in the near future.
- We will also be able to combine health knowledge graphs with medical knowledge graphs to predict the risk of diseases and future health status, and obtain more accurate information about medical conditions, including symptoms, medicine, risk factors, and doctors’ diagnoses. Doctors can use this information to achieve more rapid and accurate diagnosis.
- Technology can be used to monitor and predict the spread of infectious diseases. For example, a technology company has used natural language processing and machine learning to gather data from hundreds of thousands of public sources, including statements from official public health organizations, digital media outlets, global airline ticketing agencies, as well as livestock health reports and population demographics, to analyze the spread of disease 24 hours a day.
Personalized Treatment
Driven by digital technologies, highly personalized treatment solutions are set to become a reality in the future. Examples include how high-performance computing power and highly intelligent deep learning systems will be widely used in areas such as precision medicine, adaptive radiation therapy, and rehabilitation robots. The accuracy and speed that technology enables shifts treatment from “one-size-fits-all” to “bespoke”.
- AI can help doctors develop personalized treatment plans by analyzing thousands of pathology reports and treatment plans, and determining which would be most appropriate for each patient.
- Using that data, doctors can determine new courses of treatment for patients in real-time based on their current health status at any given moment.
- During traditional radiation therapy, radiation is directed at the general location of cancerous tissue to kill cancer cells, but since the targeted area is quite broad, the radiation typically also kills a large number of healthy cells, taking a significant toll on the patient’s body. With the help of AI technology, adaptive radiation therapy (ART) systems can automatically identify changes in lesion positioning and more accurately outline the target areas for radiation treatment. This helps focus the radiation on just the cancer cells and reduces damage to healthy tissue.
“Home-spitals“
The healthcare industry is actively exploring ways to build coordinated telemedicine systems through synergy between cloud computing, edge computing, and on-device computing. This means that portable medical devices are set to become available in grassroots-level hospitals, communities, and households. These devices collect medical data in real time and upload data to the cloud for processing, allowing users to access coordinated telemedicine services and keep track of their health from the comfort of their homes.
- Traditionally, patients go to hospitals or specialized treatment facilities for medical examinations and in-person diagnoses, which may be far away. In the near future, there may well be cloud-based diagnosis services connecting patients with top experts online, anywhere in the world.
- Doctors will soon be able to access medical imaging results and AI-assisted diagnostic tools through the cloud. Medical images, examination results, and medical records will be synchronized in real-time.
- With the application of a “device data collection + 5G + cloud computing” model, medical images can be more easily shared between community hospitals and medical centers. After images are captured on medical devices in community hospitals, they can be automatically uploaded to the cloud. Experts in medical centers can then access the images on the cloud and issue diagnostic reports.
- As components get smaller and chip technology advances, portable devices that lower the threshold for professional medical examinations could make mobile medical examinations a reality. An example of this could be a handheld ultrasound scanner, with information being collected through smartphone applications.
By 2030, technology will be enabling access to various applications that will help us stay healthier than ever before.
Stay tuned for the next week’s post on Food. Download the Intelligent World 2030 report for a deeper dive into health and for other outlooks.
This article has been adapted from the Intelligent World 2030 report.
Disclaimer: Any views and/or opinions expressed in this post by individual authors or contributors are their personal views and/or opinions and do not necessarily reflect the views and/or opinions of Huawei Technologies.
Leave a Comment