Where 5G-A Meets AI: A New Era for Telecoms
5G-Advanced and AI are converging to make telecom networks smarter, faster, and more efficient. This article explores how telcos are using the synergy to automate operations, personalize services, and unlock new revenue. In part 2, I look at real-world case studies from global operators.
5G-A and AI Synergy: The convergence that’s changing telecom
As telecom operators transition from basic connectivity providers to digital experience enablers, two powerful forces are reshaping their journey: 5G-Advanced (5G-A) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). While 5G-A delivers the next evolution in network performance – with higher speeds, improved uplink, slicing, integrated sensing and many other new advanced capabilities – AI provides the intelligent cognitive layer that enables intelligent automation, prediction, personalization, and new business models across every telecom function.
Separately, both technologies are transformational. But together, they create a compounding effect: networks that not only move faster – but think faster, respond smarter, and monetize better. Telcos across the globe – from South Korea to Kuwait – are beginning to embed AI into the very fabric of 5G-A infrastructure, unlocking new business models, operational savings, and radically improved user experiences.
This write-up aims to explore what 5G-A and AI mean in the telecom context, how their relationship is shaping the next wave of telecom innovation, and what telcos are doing today to ride this intelligent revolution.
What is 5G-A and what is AI in the telco context?
Understanding 5G-Advanced
5G-A (Release 18 and beyond in 3GPP terminology) represents the next significant evolution in 5G networks. While early 5G deployments focused on enhanced mobile broadband and foundational connectivity, 5G-A is where the real power of 5G begins to materialize – through enhanced performance, intelligence, and adaptability.
Thus, in a sense, 5G-A moves 5G closer to 6G.
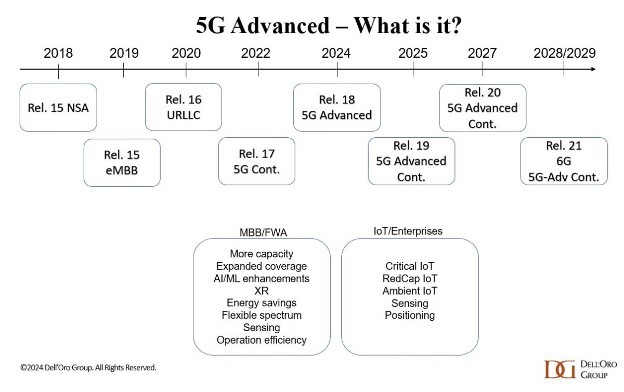
Source: 5G Technology World
A few key capabilities of 5G-A:
- Uplink boost: enhanced uplink throughput – essential for video-rich services like XR, user-generated streaming, and real-time sensors.
- RedCap (Reduced Capability): enables cost-effective, low-power connectivity for wearables, industrial sensors, and lightweight IoT devices.
- Integrated sensing: turns the network into a sensor grid that can detect movement, position, and environment – paving the way for adding further intelligence in use cases such as smart cities, traffic monitoring, and public safety.
- AI-native architecture: AI is embedded directly into network operations – from RAN to core – for the first time, enabling real-time learning, decision-making, and optimization.
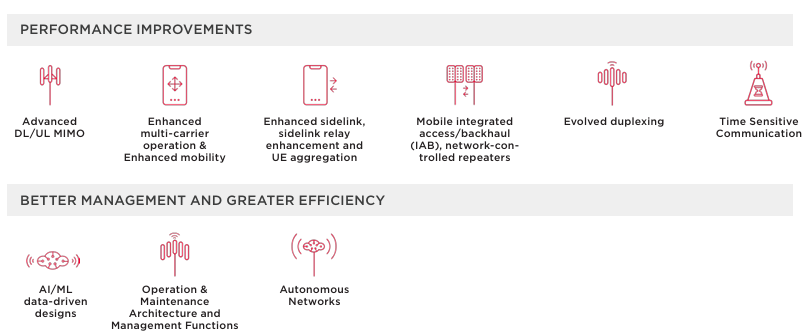
5G-A combines performance improvements and greater efficiency:
In summary, 5G-A is not just “better / faster 5G” – it’s a smarter, more responsive network layer, designed to handle the complex needs of both human and machine users in real time.
Understanding AI for telcos
AI in the telecom industry refers to a broad set of technologies – machine learning (ML), deep learning, and generative AI – that are applied to automate, optimize, and personalize various aspects of network and business operations.
Key AI applications deployed in telecoms:
· Network optimization with AI
AI helps with intelligent traffic management, dynamic spectrum allocation, energy optimization, and predictive maintenance in radio access and transport layers.
Reinforcement learning is used to self-optimize network performance based on real-time data.
· Customer service enhancement with AI
Natural language processing (NLP) powers AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants.
Generative AI (GenAI) is now enabling intent prediction, personalized service suggestions, and real-time ticket resolution.
· Customer experience enhancement with AI
Development new services or business models (such as New Calling, Real Time Translation, SLA-based services at the app level etc.)
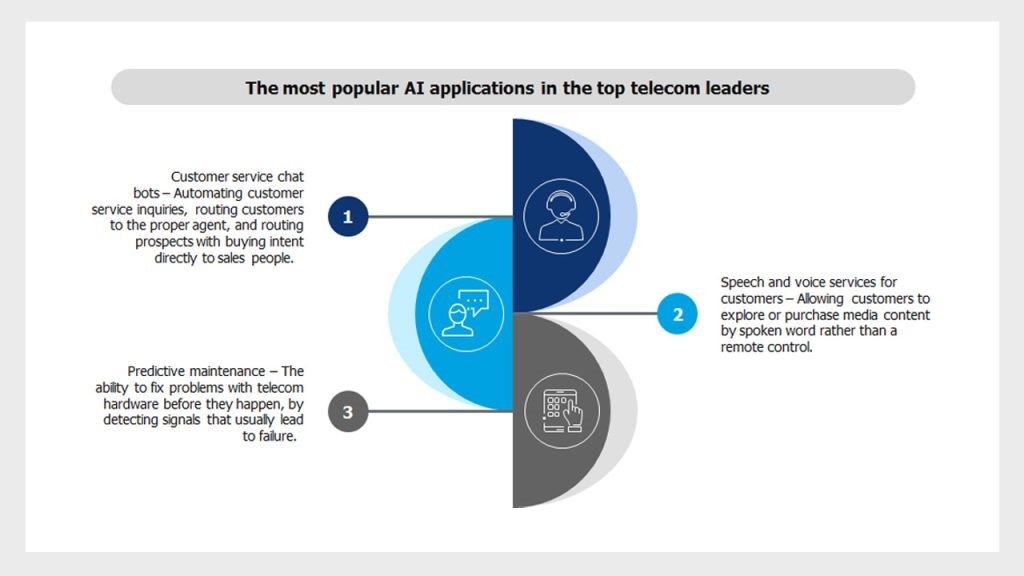
The growing maturity of AI means telecom operators are not just using AI as a tool, but are beginning to architect their networks and services around AI. This shift is most powerful when paired with a 5G-A networks, capable of hosting and supporting real-time, distributed AI functions.
The relationship between 5G-A and AI
The relationship between 5G-A and AI is not simply complementary – it’s deeply interdependent. These technologies reinforce each other’s value, forming a feedback loop where intelligent infrastructure enables advanced services, and AI empowers the network to evolve in real-time. Together, they form the intelligent engine of future telecom innovation.
AI makes 5G-A networks more potent
Unlike previous network generations, 5G-A is designed with AI built into its core. AI algorithms are increasingly responsible for managing the complexity of modern networks, where thousands of parameters (user behavior, location, service type, service experiences etc.) change in milliseconds.
How AI boosts 5G-A
- RAN optimization: AI models improve beamforming, scheduling, and interference management in massive MIMO networks, dynamically adapting to traffic loads and user mobility patterns.
- Self-healing networks: Predictive maintenance tools use AI to detect anomalies before outages occur, reducing downtime and improving service quality.
- Energy efficiency: AI enables base stations to enter low-power modes during low usage periods or reroute traffic to optimize energy use – critical for sustainability and cost control in dense 5G-A deployments.
- Network slicing automation: AI determines when and how to create, scale, or remove network slices based on real-time demand, QoS needs, and user profiles – especially in enterprise and industrial settings.
5G-A enables real-time AI
While AI empowers the network, 5G-A also empowers AI-based services and applications. Its high throughput, low latency, and edge computing capabilities allow real-time interaction and decision making.
How 5G-A Supports AI
- Edge AI inference: 5G-A’s distributed architecture allows AI models to be deployed at the network edge – closer to the user or device – reducing latency for applications like video analytics, industrial robotics, or autonomous vehicles.
- Support for massive AI workloads: AI-driven applications, such as computer vision in smart cities or voice synthesis in virtual assistants, rely on high uplink speeds and stable latency, both of which are enhanced in 5G-A.
- Integrated sensing for AI contextual awareness: With 5G-A's ability to sense location, movement, and environmental parameters, AI models gain richer context to drive decisions – e.g., adjusting traffic lights based on congestion or rerouting delivery drones around weather conditions.
Summary: The advent of AI-native networks as the “networks of tomorrow”
5G-A marks the shift from “AI-supported” to “AI-native” networks. This means:
- The network doesn’t just host AI applications – it runs on AI
- AI becomes a foundational design principle, not an add-on
- Every layer – from spectrum management to customer engagement, can evolve based on data-driven intelligence.
In practice, this results in networks that think, adapt, and improve continuously, creating not only better performance but also new business models. For example, telcos can offer AI-as-a-Service bundled with private 5G-A and edge compute, enabling hospitals to run diagnostics in real time, or manufacturers to deploy autonomous quality checks on assembly lines.
In part 2, I explore use cases from 5 global telcos where 5G-A and AI converge.
Disclaimer: Any views and/or opinions expressed in this post by individual authors or contributors are their personal views and/or opinions and do not necessarily reflect the views and/or opinions of Huawei Technologies.
Leave a Comment